Exercise Program to Prevent Falls and Frailty
1.
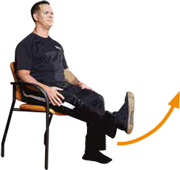
 Seated, raise one leg and straighten it as much as you can. Repeat 10 times, rest for one minute and if you can, do a second and third set of 10 repetitions each.
Seated, raise one leg and straighten it as much as you can. Repeat 10 times, rest for one minute and if you can, do a second and third set of 10 repetitions each.
2.


Bend both knees, as if going to sit down, while holding the back of a chair that is resting against a wall to avoid having it move.
Repeat 10 times, rest for one minute and if you can, do a second and third set of 10 repetitions each.
3.

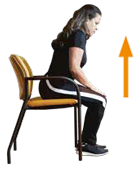
Press your feet firmly on the floor and stand up from a chair without touching the armrests. Repeat 10 times, rest for one minute and if you can, do a second and third set of 10 repetitions each. If you are having trouble, start by using the armrests if needed.
4.

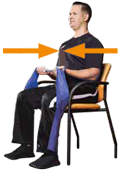 Grab an elastic band and hold it in each hand or roll it around your wrists. Open your arms rotating these outwardly. Repeat 10 times, rest for one minute and if you can, do a second and third set of 10 repetitions each.
Grab an elastic band and hold it in each hand or roll it around your wrists. Open your arms rotating these outwardly. Repeat 10 times, rest for one minute and if you can, do a second and third set of 10 repetitions each.
5.
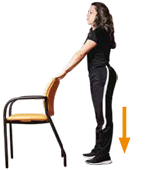

Stand up and while holding on to something raise your heels off the floor balancing on your toes for 10 seconds.
Repeat 10 times, rest for one minute and if you can, do a second and third set of 10 repetitions each.
6.

Walk for 15 minutes, resting if necessary. You may start with 4 minute intervals until you can do 15 minutes without stopping to rest.
If you can, do two more 15 minute sets. Your goal is to walk anywhere between 15 and 30 minutes continuously at least once a day.
You should do these exercises at least 5 times per week.
You should consult your doctor before engaging in this exercise program. Please talk to your doctor about any contraindications. If your doctor has told you not to engage in physical activity or exercise, please wait until your doctor gives you the all-clear to start exercising and ask if you could do the exercises illustrated here.
Contraindications:
- Recent heart attack or unstable angina
- Uncontrolled or untreated arrhythmias – such as atrial fibrillation
- Descending aortic aneurysm
- Severe aortic stenosis
- Acute endocarditis or pericarditis
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Acute deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism
- Acute heart failure
- Acute respiratory failure
- Uncontrolled hypotension
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia
- Recent fracture (last 3 months)
- Untreated infections
- Any pathology that causes significant functional impairment
- Balance disorder
